前回の画面録画の紹介で、ちょっとadbコマンドを使った。でも、adbコマンドをちゃんと紹介していなかったので、順番は前後してしまうが、今回は、adbコマンドのさわりの部分を解説することにしよう。どうして「さわり」なのかというと、adbコマンドには、かなり多くサブコマンドがあり、そのうちの1つで、前回使った「adb shell」は、Linuxのシェルそのものなので、これを解説するだけで本一冊ぐらいになってしまうもの。この連載だとどうしても最初は「さわり」だけになってしまうのである。
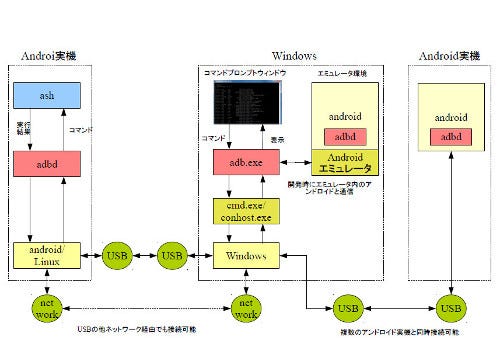
adbとは、「android debug bridge」の略。adbは、PCを使ってアンドロイドを開発する場合に、アンドロイド側との通信を受け持ち、さまざまな機能を提供する(図01)。実際には、アンドロイド側で動作しているadbd(adb deamon)と通信を行い、実際の処理はadbd側で行い、その実行メッセージなどをadbへ返して、adbがコマンドプロンプトウィンドウ内でメッセージを表示する。adbなどの記述だと、adb.exeを実行しているPC側を「ローカル」、USBケーブルなどで接続されているアンドロイド側を「リモート」と呼ぶ。以後の説明もこの用語を使う。なお、adb.exeを実行しているPCには複数のアンドロイド機を同時に接続することが可能で、また、PC上で実行しているエミュレータにも接続ができる。
|
図01: adbは、ウィンドウズ側のadb.exeとアンドロイド側のadbdがUSBやネットワークで通信し、実際の処理はadbd側で行い、その実行メッセージなどをadbへ返して、adbがコマンドプロンプトウィンドウ内でメッセージを表示 |
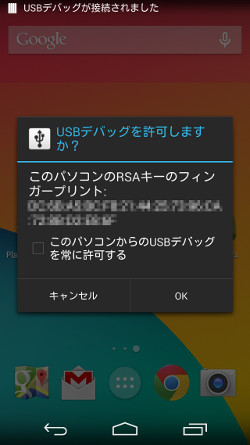
adb.exeは、ローカル側でバックグラウンドで動作しており、USBケーブルなどの接続を監視していて、アンドロイドデバイスが接続されるのを待つ。USBによる接続では、アンドイロドを接続したらデバイスドライバが組み込まれ、デバイスとしてWindowsが認識する。その上で、adb.exeがリモートのadbdに接続できないと、adbの機能が実行できるようにならない。なお、現在では、リモート側で、接続するPCを認証するようになっているため、初回の接続で、ダイアログボックス(写真01)が出て、ユーザーが確認しないと、adb.exeからは認識が完了しない。ダイアログボックスには、接続したPCを記憶するチェックボックスがあるので、常に利用するならチェックボックスをオンにしてからOKボタンを押す。これをしないと、毎回、接続時にダイアログボックスが表示されるようになる。
|
写真01: 開発オプションでUSBデバッグをオンにして、PCにUSB接続すると、最初にダイアログボックスが表示され、接続したPCでデバッグを行うかどうかを確認する。チェックボックスをオンにして「OK」を押すと、該当のPCに再度接続しても確認しなくなる |
現在接続されてadb.exeに認識されているデバイスを表示するには、以下のコマンドのどちらかを利用する。
adb devices
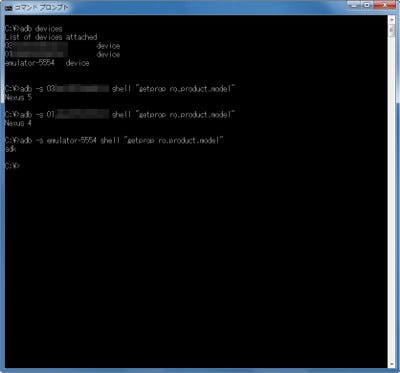
adb -lこのコマンドを実行すると、接続しているデバイスの一覧とそのIDが表示される(写真02)。リモートが1つしかない場合には、何も指定せずにadb.exeのサブコマンドを実行できるが、複数ある場合には、IDを指定してサブコマンドを実行させる。このときの書式は、
adb -s デバイスのID サブコマンドとなる。複数の実機やエミュレータを同時に接続、起動して、adbコマンドから利用が可能だ。
|
写真02: adb devicesコマンドで接続しているデバイスやエミュレータの一覧を取得、その後、-sオプションでデバイスIDを指定してそれぞれで別々のadbコマンドを実行させることができる。ただし、adb shellはコンソールを占有するため、別のウィンドウを開く必要がある |
ただし注意することがある。adbサブコマンドのほとんどは、リモート側のアンドロイドで実行されるが、表示されるのはウィンドウズ側になっていることだ。アンドロイドとウィンドウズではシステムとしての違いがあるため、コマンドやその引数がどちらのものなのかを常に意識する必要がある。
たとえば、ウィンドウズではパスの区切り文字には、「\」を使うが、アンドロイドでは「/」だ。このため、アンドロイド側のファイルをウィンドウズ側にコピーするコマンドでは、コピー元になるファイルの指定は、アンドロイドの方式で行うが、ローカル側の指定はウィンドウズ方式で行う。
前回紹介したリモート側からのファイルコピーは、
adb pull リモートパス ローカルパスとなるため、たとえば、
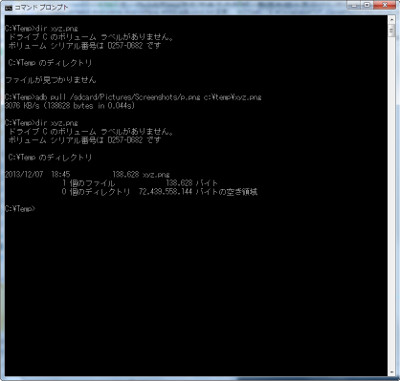
adb pull /sdcard/Pictures/Screenshots/p.png c:\temp\Input-Here\xyz.pngは、リモート側の「sdcard/Pictures/Screenshots/p.png」というファイルをローカル側の「c:\temp\」フォルダに「xyz.png」という名前でコピーするコマンドになる(写真03)。
|
写真03: adb pullコマンドでアンドロイド側のファイル(/sdcard/Pictures/Screenshots/p.png)をウィンドウズ側にc:\temp\Input-Here\xyz.pngとしてコピーした場合の実行例 |
なお、pullサブコマンドの場合、ローカル側のパス指定を省略すると、カレントディレクトリにリモート側と同じ名前のファイルがコピーされる。前回紹介したコマンドでは、これを使ってローカル側のファイル指定を省略していた。
また、アンドロイドとウィンドウズでは、標準のテキストファイルで使う日本語などのマルチバイト文字コードも違うため、shellサブコマンドで表示を行わせようとすると、日本語などのマルチバイト部分が文字化けする(英数字などの1バイトコードは表示可能)。これは、アンドロイド側の文字コードがUTF-8なのに対して、コマンドプロンプトは、2バイト文字コードとしてはSJISコードを想定しているためだ。ウィンドウズのコマンドプロンプトウィンドウでは、簡単にUTF-8のマルチバイト文字を表示させることはできないため、ファイル内容を確認するには、UTF-8を解釈できるプログラムをローカル側で用意する必要がある。
adbコマンドには、数多くの「サブコマンド」があり、「adb サブコマンド」とスペースを置いてサブコマンドを指定すれば、さまざまな機能が利用できる。どのようなサブコマンドがあるのかは、SDKのバージョンよって違っているが、「adb help」で確認可能だ(下記参照、adb helpサブコマンドによるadbのヘルプ表示。さまざまなコマンドがある)。
C:\>adb help
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.31
-a - directs adb to listen on all interfaces for a connection
-d - directs command to the only connected USB device
returns an error if more than one USB device is present.
-e - directs command to the only running emulator.
returns an error if more than one emulator is running.
-s - directs command to the device or emulator with the given
serial number or qualifier. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL
environment variable.
-p - simple product name like 'sooner', or
a relative/absolute path to a product
out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'.
If -p is not specified, the ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT
environment variable is used, which must
be an absolute path.
-H - Name of adb server host (default: localhost)
-P - Port of adb server (default: 5037)
devices [-l] - list all connected devices
('-l' will also list device qualifiers)
connect [:] - connect to a device via TCP/IP
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
disconnect [[:]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device.
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
Using this command with no additional arguments
will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices.
device commands:
adb push - copy file/dir to device
adb pull [] - copy file/dir from device
adb sync [ ] - copy host->device only if changed
(-l means list but don't copy)
(see 'adb help all')
adb shell - run remote shell interactively
adb shell - run remote shell command
adb emu - run emulator console command
adb logcat [ ] - View device log
adb forward --list - list all forward socket connections.
the format is a list of lines with the following format:
" " " " "\n"
adb forward - forward socket connections
forward specs are one of:
tcp:
localabstract:
localreserved:
localfilesystem:
dev:
jdwp: (remote only)
adb forward --no-rebind
- same as 'adb forward ' but fails
if is already forwarded
adb forward --remove - remove a specific forward socket connection
adb forward --remove-all - remove all forward socket connections
adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport
adb install [-l] [-r] [-s] [--algo --key --iv ]
- push this package file to the device and install it
('-l' means forward-lock the app)
('-r' means reinstall the app, keeping its data)
('-s' means install on SD card instead of internal storage)
('--algo', '--key', and '--iv' mean the file is encrypted already)
adb uninstall [-k] - remove this app package from the device
('-k' means keep the data and cache directories)
adb bugreport - return all information from the device
that should be included in a bug report.
adb backup [-f ] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] []
- write an archive of the device's data to .
If no -f option is supplied then the data is written
to "backup.ab" in the current directory.
(-apk|-noapk enable/disable backup of the .apks themselves
in the archive; the default is noapk.)
(-obb|-noobb enable/disable backup of any installed apk expansion
(aka .obb) files associated with each application; the default
is noobb.)
(-shared|-noshared enable/disable backup of the device's
shared storage / SD card contents; the default is noshared.)
(-all means to back up all installed applications)
(-system|-nosystem toggles whether -all automatically includes
system applications; the default is to include system apps)
( is the list of applications to be backed up. If
the -all or -shared flags are passed, then the package
list is optional. Applications explicitly given on the
command line will be included even if -nosystem would
ordinarily cause them to be omitted.)
adb restore - restore device contents from the backup archive
adb help - show this help message
adb version - show version num
scripting:
adb wait-for-device - block until device is online
adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - prints:
adb get-devpath - prints:
adb status-window - continuously print device status for a specified device
adb remount - remounts the /system partition on the device read-write
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program
adb reboot-bootloader - reboots the device into the bootloader
adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions
adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB
adb tcpip - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port
networking:
adb ppp [parameters] - Run PPP over USB.
Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection.
refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
adb sync notes: adb sync [ ]
can be interpreted in several ways:
- If is not specified, both /system and /data partitions will be updated.
- If it is "system" or "data", only the corresponding partition
is updated.
environmental variables:
ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values
1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given.
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed.
E:\CloneData\TXT_Clone\NikkeiBP\PC-Online\Mobile\20131204#291-Kindle-PaperWhite\Figure>adb -v
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.31
-a - directs adb to listen on all interfaces for a connection
-d - directs command to the only connected USB device
returns an error if more than one USB device is present.
-e - directs command to the only running emulator.
returns an error if more than one emulator is running.
-s - directs command to the device or emulator with the given
serial number or qualifier. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL
environment variable.
-p - simple product name like 'sooner', or
a relative/absolute path to a product
out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'.
If -p is not specified, the ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT
environment variable is used, which must
be an absolute path.
-H - Name of adb server host (default: localhost)
-P - Port of adb server (default: 5037)
devices [-l] - list all connected devices
('-l' will also list device qualifiers)
connect [:] - connect to a device via TCP/IP
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
disconnect [[:]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device.
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
Using this command with no additional arguments
will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices.
device commands:
adb push - copy file/dir to device
adb pull [] - copy file/dir from device
adb sync [ ] - copy host->device only if changed
(-l means list but don't copy)
(see 'adb help all')
adb shell - run remote shell interactively
adb shell - run remote shell command
adb emu - run emulator console command
adb logcat [ ] - View device log
adb forward --list - list all forward socket connections.
the format is a list of lines with the following format:
" " " " "\n"
adb forward - forward socket connections
forward specs are one of:
tcp:
localabstract:
localreserved:
localfilesystem:
dev:
jdwp: (remote only)
adb forward --no-rebind
- same as 'adb forward ' but fails
if is already forwarded
adb forward --remove - remove a specific forward socket connection
adb forward --remove-all - remove all forward socket connections
adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport
adb install [-l] [-r] [-s] [--algo --key --iv ]
- push this package file to the device and install it
('-l' means forward-lock the app)
('-r' means reinstall the app, keeping its data)
('-s' means install on SD card instead of internal storage)
('--algo', '--key', and '--iv' mean the file is encrypted already)
adb uninstall [-k] - remove this app package from the device
('-k' means keep the data and cache directories)
adb bugreport - return all information from the device
that should be included in a bug report.
adb backup [-f ] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] []
- write an archive of the device's data to .
If no -f option is supplied then the data is written
to "backup.ab" in the current directory.
(-apk|-noapk enable/disable backup of the .apks themselves
in the archive; the default is noapk.)
(-obb|-noobb enable/disable backup of any installed apk expansion
(aka .obb) files associated with each application; the default
is noobb.)
(-shared|-noshared enable/disable backup of the device's
shared storage / SD card contents; the default is noshared.)
(-all means to back up all installed applications)
(-system|-nosystem toggles whether -all automatically includes
system applications; the default is to include system apps)
( is the list of applications to be backed up. If
the -all or -shared flags are passed, then the package
list is optional. Applications explicitly given on the
command line will be included even if -nosystem would
ordinarily cause them to be omitted.)
adb restore - restore device contents from the backup archive
adb help - show this help message
adb version - show version num
scripting:
adb wait-for-device - block until device is online
adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - prints:
adb get-devpath - prints:
adb status-window - continuously print device status for a specified device
adb remount - remounts the /system partition on the device read-write
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program
adb reboot-bootloader - reboots the device into the bootloader
adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions
adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB
adb tcpip - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port
networking:
adb ppp [parameters] - Run PPP over USB.
Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection.
refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
adb sync notes: adb sync [ ]
can be interpreted in several ways:
- If is not specified, both /system and /data partitions will be updated.
- If it is "system" or "data", only the corresponding partition
is updated.
environmental variables:
ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values
1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given.
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed. 本稿は、2013年12月9日にAndorid情報のWeb専門誌「AndroWire」に掲載した記事を再構成したものです。









